The short answer about the dinosaur size is – they had more food around.
But let’s dive deeper and answer other questions we already starting to have!
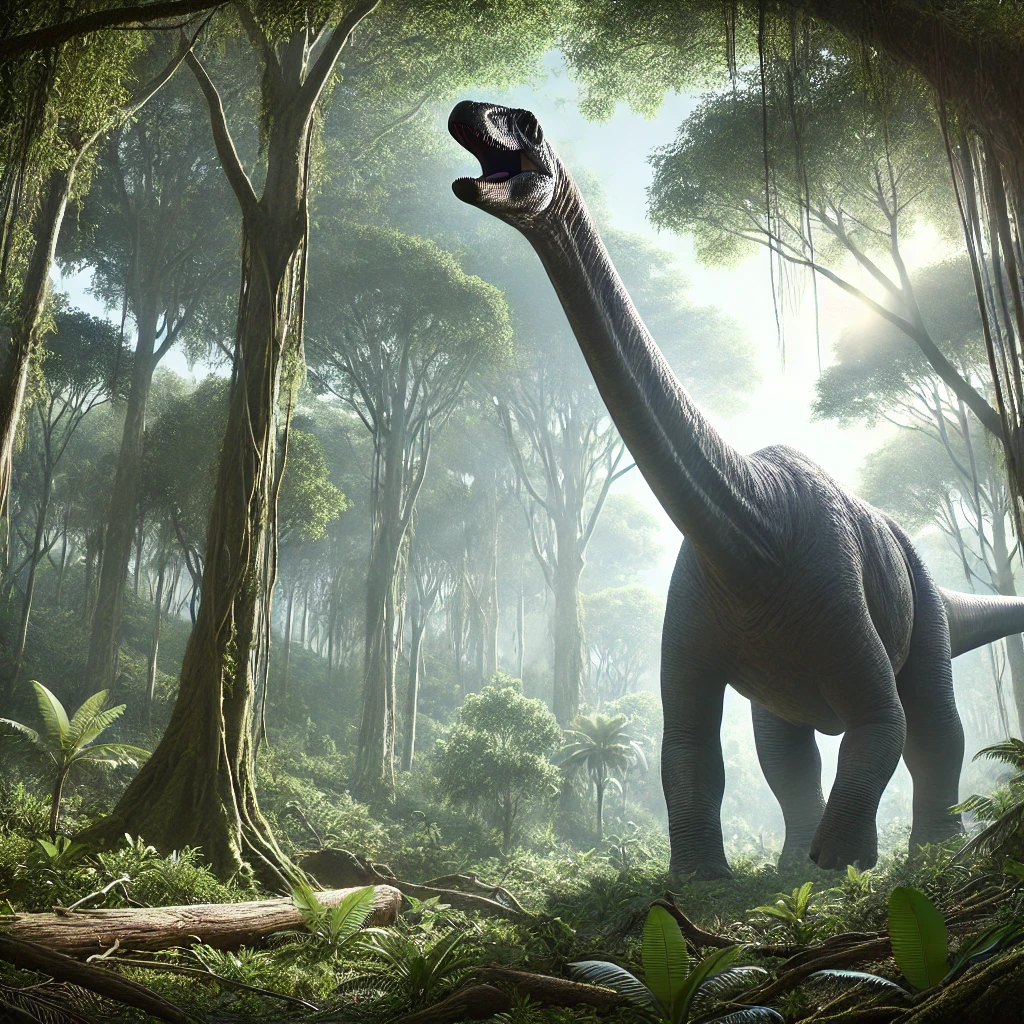
Dinosaurs are often remembered for their immense size. Some species, like the Brachiosaurus, could grow up to 85 feet long and weigh as much as 40 tons. The question is: Why did dinosaurs become so gigantic? Let’s explore some of the reasons behind their colossal size.
Environmental Factors
During the Mesozoic era, the Earth’s atmosphere and climate were vastly different from today. It is believed that higher levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide created a greenhouse effect, leading to warmer temperatures and lush vegetation. These conditions allowed herbivorous dinosaurs to grow larger because food was abundant. With so much vegetation to feed on, herbivores like the Brachiosaurus could sustain their massive bodies.
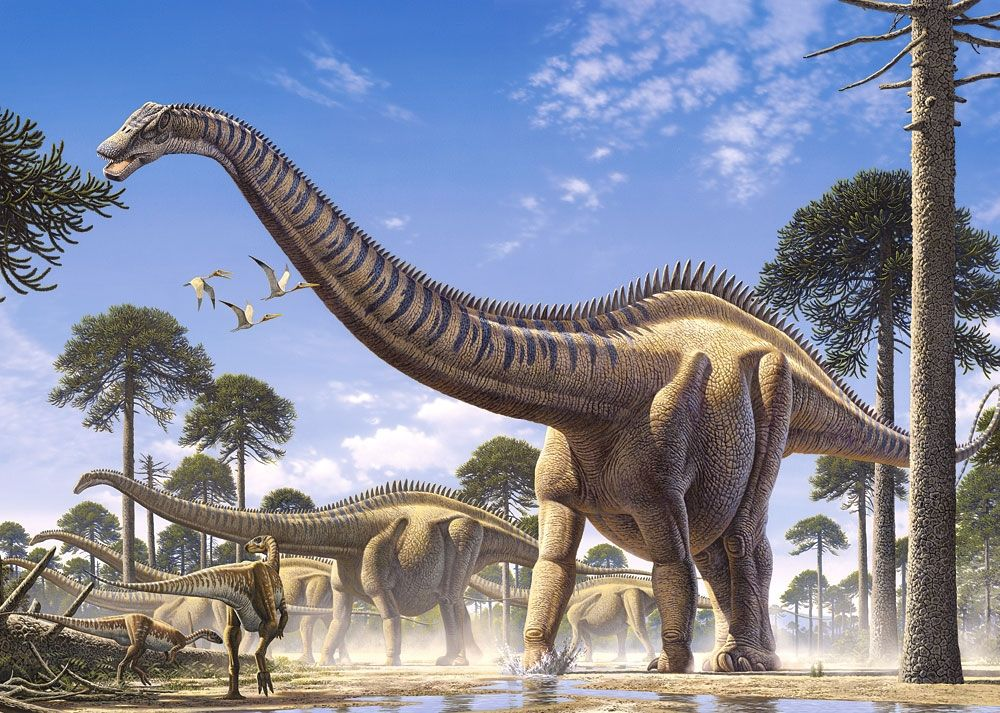

Evolutionary Arms Race
Dinosaurs were involved in an evolutionary arms race, where predators and prey kept getting larger as a survival tactic. Larger predators, like the Tyrannosaurus Rex, could take down bigger prey, but herbivores evolved to grow even larger to defend themselves. This constant pressure drove both carnivores and herbivores to reach massive sizes, ensuring that only the biggest and strongest survived.
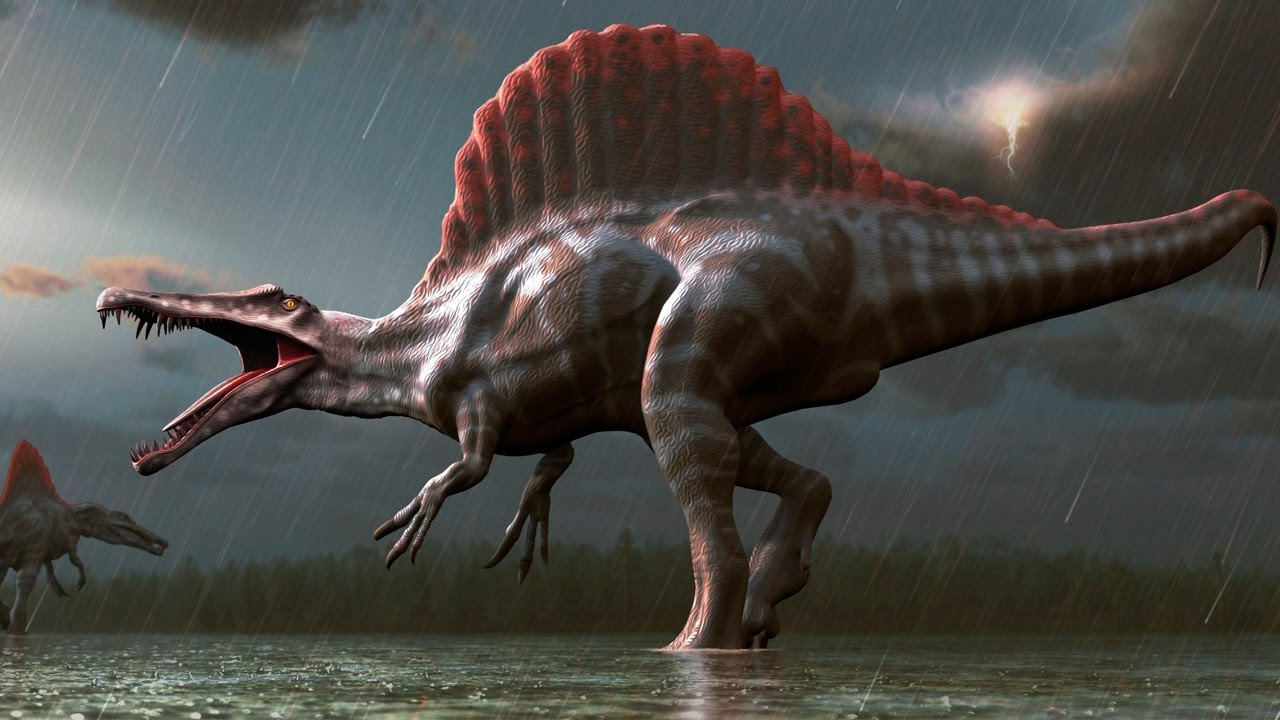

Efficient Lungs and Metabolism
Many scientists believe that dinosaurs had a highly efficient respiratory system similar to modern birds. Their unique lungs allowed them to breathe more efficiently and provided the oxygen needed to support their large bodies. Additionally, their metabolism may have been somewhere between reptiles and mammals, allowing them to grow faster and larger without overheating or requiring excessive energy.
These factors, among others, contributed to the gigantic size of dinosaurs, making them some of the largest creatures ever to walk the Earth. Their impressive dinosaur size helped them dominate their environments for millions of years before their eventual extinction.